How Data Analysts Help Organizations Get Maximum Value from SAP
In today’s data-driven business environment, SAP plays a critical role in helping organizations manage their core operations such as finance, supply chain, human resources, sales, and production. However, the true power of SAP is unlocked only when data is effectively analyzed and transformed into meaningful insights. This is where a data analyst becomes essential. A data analyst acts as the bridge between raw SAP data and strategic business decisions, ensuring organizations gain measurable value from their SAP investments. By analyzing structured and transactional data generated within SAP systems, data analysts help businesses improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance performance, and remain competitive.
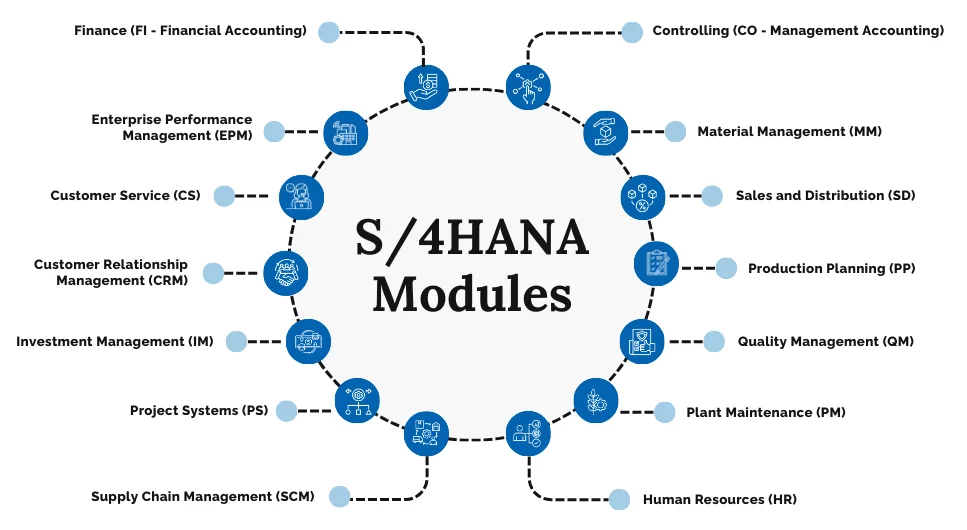
SAP systems generate massive volumes of data every day across different modules such as SAP FI, CO, MM, SD, HCM, and S/4HANA. A data analyst helps extract, clean, and structure this data using SAP tools like SAP BW, SAP HANA, SAP Analytics Cloud, and external analytics platforms such as Power BI or Tableau. Without proper analysis, this data remains underutilized. Data analysts design dashboards, reports, and visualizations that allow stakeholders to clearly understand trends, anomalies, and performance metrics. These insights help management make faster and more informed decisions based on real-time and historical data.
One of the most important ways data analysts help SAP-driven organizations is through performance monitoring and optimization. SAP systems track key performance indicators (KPIs) across business processes. A data analyst identifies relevant KPIs, monitors them regularly, and highlights inefficiencies or risks. For example, in supply chain management, analysts can identify delays, inventory shortages, or excess stock. In finance, they can analyze cost overruns, revenue leakage, or profitability trends. These insights allow business leaders to take corrective actions before small issues turn into major problems.
Data analysts also play a crucial role in SAP data quality and governance. SAP systems rely heavily on accurate master and transactional data. Poor data quality can lead to incorrect reporting, compliance issues, and financial losses. Data analysts help define data standards, validate data accuracy, and identify inconsistencies or duplicates across SAP modules. By ensuring data integrity, analysts help organizations trust their SAP reports and analytics, which is essential for regulatory compliance and strategic planning.
Another key contribution of data analysts in SAP environments is predictive and prescriptive analytics. Using historical SAP data combined with advanced analytics techniques, analysts can forecast future trends such as demand patterns, sales growth, cash flow, or production requirements. Predictive insights help organizations proactively plan resources and reduce uncertainty. Prescriptive analytics goes a step further by recommending optimal actions, such as adjusting pricing strategies, optimizing inventory levels, or improving workforce planning. These advanced insights significantly enhance the strategic value of SAP.
SAP transformations and migrations, such as moving from ECC to S/4HANA, also heavily depend on data analysts. During such projects, analysts assess existing data, identify obsolete or redundant information, and ensure clean data migration. Post-migration, they validate reports and dashboards to ensure accuracy and continuity. Their involvement reduces project risks, shortens implementation timelines, and ensures the new SAP system delivers expected business outcomes.
In addition, data analysts help customize SAP reporting to meet the unique needs of different departments. Standard SAP reports may not always address specific business questions. Analysts work closely with business users to understand requirements and develop customized reports and dashboards. This user-centric approach improves adoption of SAP analytics tools and empowers employees at all levels to make data-driven decisions.
In conclusion, a data analyst plays a vital role in helping organizations fully leverage SAP systems. By transforming complex SAP data into actionable insights, ensuring data quality, enabling performance monitoring, and supporting advanced analytics, data analysts maximize the return on SAP investments. Organizations that effectively integrate data analysts into their SAP ecosystem are better positioned to achieve operational excellence, strategic agility, and long-term business success.